Introduction
We will explore the importance of having a detailed backup plan for your business’s survival, the critical information that needs to be kept, and the differences between cloud storage and cloud backup. Also, we will cover key topics like why platforms like Microsoft 365 do not automatically backup data, efficient backup planning strategies, and the importance of off-site backups. Furthermore, we will review backup technologies, disaster recovery plans, and the significance of regularly testing your backups to ensure business continuity.
In the end, you will understand how to create a reliable backup plan that protects both your data and your company.
Table of Contents
Why you need a backup plan for your business data
Nobody wants to think about losing data. However, there is a real danger of it happening, whether that’s due to equipment failure, unintentional deletion, virus infection, or cyber security incidents. The best way to prevent loss of data is to have an up-to-date, secure, and immediately available backup.
There are many reasons why you might be unable to access your data:
- Your device is lost or stolen.
- Your device breaks.
- Your hard drive needs to be erased or replaced.
- You have a new device, and you want to copy existing files onto it.
- A virus (or other type of malware, such as ransomware), may erase your data or prevent you from accessing it.
What does backup mean? In computing, a copy of a file or other item of data made in case the original is lost or damaged.
There are many methods for backing up business data, saving to physical tapes or discs and storing away from the machine or using the availability of cloud storage, which in recent years has changed how people perform data backup procedures.
In the past, backing up data has been seen as a chore, but today having a backup of your data can be critical to business survival if disaster strikes. There are other factors to consider when developing a backup strategy and a larger disaster recovery plan , which we will discuss in more detail.
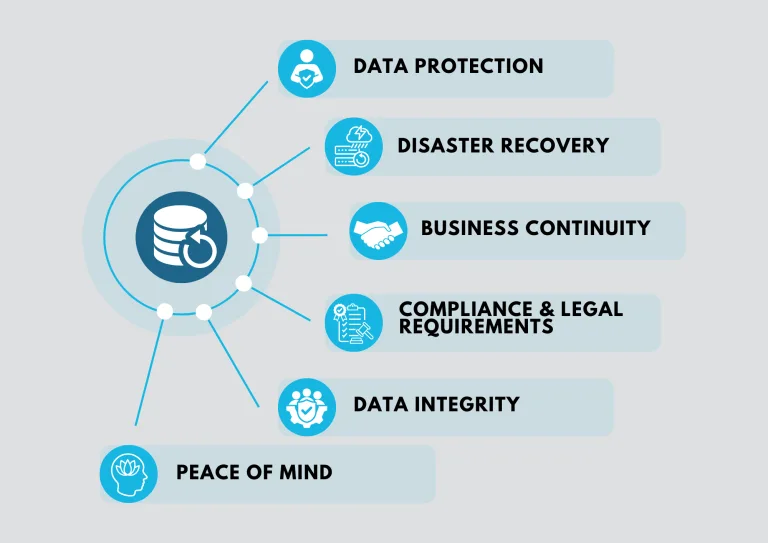
There are numerous reasons why backups are crucial, such as:
- Data Protection: Backups serve as a safety net for your valuable data. They protect against data loss due to various factors like hardware failure, software glitches, human error, malware attacks, or natural disasters.
- Disaster Recovery: In the event of data loss or system failure, backups enable quick recovery. By restoring data from a backup, you can minimise downtime and resume normal operations faster.
- Business Continuity: Backups are crucial for maintaining uninterrupted business operations. Having reliable backups ensures that critical data and systems can be restored promptly, reducing the impact of disruptions on productivity and customer service.
- Compliance and Legal Requirements: Many industries have specific data retention and compliance regulations. Backups help organisations meet these requirements and provide a means to recover data if needed for legal or regulatory purposes.
- Data Integrity: Backups preserve data integrity by capturing a point-in-time snapshot of information. This allows you to revert to a previous state or recover specific files or data elements as required.
- Peace of Mind: Regular backups provide peace of mind, knowing that your important files, documents, and data are securely stored and can be restored if necessary. This reduces anxiety and minimises the potential consequences of data loss.
Remember, it is important to regularly test and verify the effectiveness of backups to make sure they are reliable and useful in case of emergencies.
Identify what needs to be backed up
A misconception is that backing up data is simply about saving as much information as frequently as possible. Although this holds some truth, it is crucial to delve deeper into what should be saved and for what reasons, so your initial focus should be on identifying the systems and data requiring backup.
It is crucial to start with the central server, where most of your data is stored. Which services are essential to your everyday business? What business systems can you not do without?
Next it will be necessary to regularly backup production files, files that are worked on every day and will need either daily or more often, depending on the technology being utilised.
Program and operating system files may require less frequent backups. Typically, monthly backup is enough, but it’s important to also be able to create additional backups before and after making upgrades and changes.
Determine if it is necessary to back up data stored on individual computers and devices. Even though most of your essential business data may be stored on servers, documents like emails, spreadsheets, could be saved locally. It is important to assess their value, determine if they need to be backed up, and decide on the frequency of backups.
Do you want to keep your company up and running, even when there are serious threats to your stability?
Did you know that Microsoft doesn't backup your 365 data?
What about everything in the cloud? Backing up Office 365 is very important; it helps protect your data from loss and potential corruption and makes sure it is recoverable.
Despite what people may think, data in the cloud can still be lost. Backing up your Microsoft 365 data is not a minor consideration but a crucial requirement for your business. The importance of Microsoft 365 applications is growing as companies use SharePoint Online and Microsoft Teams more.
Backing up your Microsoft 365 data is necessary for more than just retrieving lost or deleted files. Here are six reasons why it is crucial to backup Microsoft 365:
- Accidental deletion: Accidental deletion, modification, or overwriting of data can be disastrous. With a backup plan, you can rapidly recover lost data and maintain business operations without disruptions.
- Confusion and gaps in retention policies: Microsoft’s retention policies are intricate, making them challenging to understand and follow accurately. This can put your data in danger of being lost once the retention period ends.
- Internal security risks: The possibility of internal threats, such as unhappy employees erasing important data, is reasonable and should not be missed. A backup option offers protection in such circumstances.
- Outside security risks: Malware and ransomware have the potential to seriously harm to your company’s data and reputation. Frequent backups guarantee there is always a clean version of your data available for restoration.
- Meeting legal and compliance requirements: A strong backup system can prevent your company from facing legal issues by allowing you to access data needed for legal and compliance reasons.
- Managing hybrid email deployments and migrations: The correct Microsoft 365 backup solution must be capable of managing hybrid email deployments and migrations, regardless of the source location.
Learn more about Microsoft Office 365 and Backups.
What is cloud backup?
Cloud backup involves creating duplicates of your files, applications, or database, to a different location on physical servers in data centres to enable recovery in case of a security breach, system failure, outage, or natural disaster. This ensures that your business continues to operate normally, even during times of crisis.
Cloud backup, also called online or remote backup, serves as a safeguard in case of important information loss. It allows your business to quickly resume operations following a data disaster. This assists in reducing the consequences of data loss and downtime for your business.
Cloud Backup VS Cloud Storage
Cloud backup and cloud storage are commonly used terms used interchangeably, despite having different functions. Cloud backup safeguards your data from loss or harm by producing remote duplicates for emergency restoration. However, cloud storage operates similarly to an external hard drive located off-site, offering the ability to share files and access them from anywhere. Cloud storage is commonly used in subscription services like Amazon Cloud Drive, Apple iCloud, Dropbox, Google Drive, and Microsoft OneDrive, to name but a few.
Cloud storage allows for convenient retrieval of data regardless of device limitations, removing the need for extra equipment, and you can upgrade your subscription plan at any point to increase storage capacity based on your company’s needs. However, one significant issue is that you manually choose files and folders you wish to save to the cloud.
A common misconception is that cloud storage is automatically backed up; however, this is usually not true. Cloud storage services such as Google Drive, SharePoint, Azure, or Dropbox provide a convenient online location to store your files but don’t provide the necessary protection against accidental deletion, damage, or hacking. If your files are affected, they may be lost forever unless you have established a backup system.
Don’t assume your data stored in the cloud is backed up; assume it isn’t and add cloud data to your list of what needs to be backed up.
Planning your backups
Once you have determined what needs to be backed up, the next step is to decide how frequently it should be done. The frequency of saving data depends on its importance to your business: the more crucial the data, the more frequent the backups should be.
The standard recommendation is to follow a 3-2-1 backup method, which suggests having three duplicates of each file, with at least one stored off-site. This could indicate that you have a duplicate of your original work saved on two different backup devices, or one on a backup device locally and another stored in the cloud.
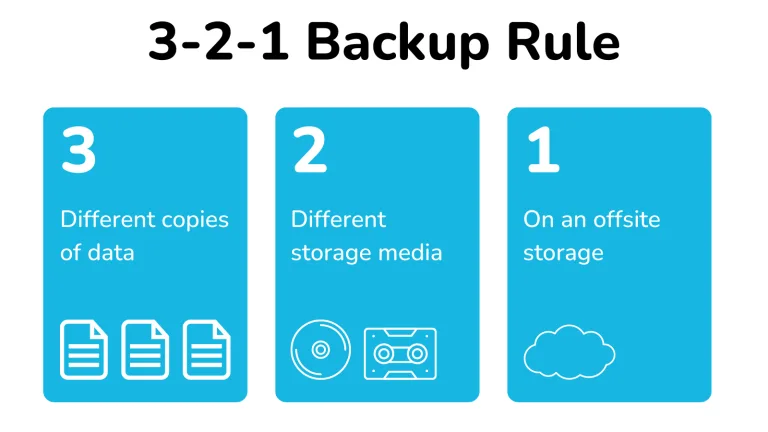
The 3-2-1 backup rule is a widely recommended approach for data backup and recovery. It consists of the following principles:
- Three Copies: Keep at least three copies of your data. This includes the original data and two additional backups.
- Two Storage Media: Store the copies on at least two different types of storage media to minimise the risk of data loss. For example, you could have one copy on your primary storage device (e.g., your computer’s hard drive) and another on an external hard drive or cloud storage.
- One Off-site Location: Store at least one backup copy in an off-site location, separate from the original data and local backups. This protects against disasters like fire, theft, or other localised events that could affect all your data.
Following the 3-2-1 backup rule helps to ensure redundancy, protection against various types of data loss scenarios, and an increased chance of successful data recovery.
Why have off site backups
It’s crucial always to keep backups separate from the system they are associated with. This implies that if there is a fire, theft, or any unexpected issues, you will not lose both your main system and your backup.
Forms of off-site backup could be,
- Subscription-based cloud storage
- Private cloud storage (a computer located separately but connected via a network connection)
- Tape drive backup (local) and store in a separate location
- External USB hard drive (local), stored in a separate location
Some of these off-site solutions are time-consuming and rely heavily on human intervention and hardware. Utilising cloud technology for your off-backup can result in making backups less cumbersome, more easily adaptable to your company’s data needs and happening automatically. Nevertheless, you may wish to contemplate storing your most important files on a local device, like an external hard drive, for additional peace of mind.
If your business data is sensitive, you should consider the security measures for your backup copies. Is it essential to encrypt the data as you store it, for instance? When utilising cloud storage, assess the security protocols of your provider.
Backup technologies
The traditional method has been to use tape or an external disc to store backups and backup software to manage the files, folders, and schedule of the backup. It would involve making multiple duplicates of the media to revisit previous file versions and a system involving three generations of data being constantly replaced in order.
It requires constant human intervention to swap out the media in this hardware data backup approach. Although the backup software may be automated to run on a schedule, someone needs to ensure the correct disk is connected at the designated time, leading to a higher chance of errors.
Cloud backup storage helps to resolve a lot of these issues. Backups can be automated with little need for manual assistance. Files can be constantly backed up to capture changes immediately.
There are advantages in scalability as well as there is no requirement to purchase additional or bigger disks as the volume of data requiring backup increases.
Naturally, the quality of a cloud backup depends on the reliability of the company offering it. Not just the cost factors, but the backup provider’s location, performance, and security measures need to be considered.
Be aware for instance, that certain sensitive data cannot be stored outside of the UK due to compliance regulations, so it is important to assess the available data restoration mechanisms in case they are needed.
Something else to consider is how easy to restore a single file, if it is accidentally damaged or destroyed, instead of having to restore the whole library.
There are multiple reasons for data retention, especially when it comes to compliance with regulations. Cloud backups are an excellent way to address compliance concerns, although caution is still needed.
Download our free Disaster Recovery Plan Checklist
Testing the Backup
Why do we need to test the backup? If we can’t successfully restore files from the backup after a system failure or some other type of disaster, then your business risks catastrophe, including the possibility of fines and lawsuits.
By testing backups, you can check that essential data is stored accurately and preserved for later use. If a test fails, there is time to fix the problem before the data is lost forever. One other benefit is that it also verifies the effectiveness of the backup policies, procedures, and schedule. How often you test is just as important as the schedule you choose to backup your data. As we have already discussed, the importance of the data dictates how often it needs to be backed up. So, your testing schedule should also be geared to the importance and type of data.
Backup planning
What is backup planning?
If you are unsure of what to consider when it comes to what a backup strategy involves? Then you should keep in mind that backup planning is simply the process of creating and implementing a blueprint that ensures your important data and systems can be restored in the event of a failure or disaster.
As we have already described in the previous sections, this includes regularly creating backups of important data and systems, as well as testing and updating the plan to ensure it remains effective. The goal of backup planning is to minimise the risk of data loss and minimise the time it takes to restore systems and data in the event of a failure.
4 Steps to creating a backup plan
Planning for data backup is a crucial part of managing data and preparing for failures or disasters. This can include recognising the important information and systems that require safeguarding, deciding on suitable backup techniques and creating a routine for consistently producing and assessing backups.
Step 1: Define the length of your data
The starting point in creating a data backup plan should be to define the range and identify the vital information and systems that need to be protected. This includes key business and financial information, customer information, and any other data required for the company’s operations.
Step 2: Decide how often to backup data
Next, you must determine a schedule for regularly creating and testing data backups. This schedule should be based on the importance of the data and systems being protected and should consider the potential impact of data loss.
Step 3: Choose a data backup option
Lots of technologies, such as full backups, incremental backups, and differential backups, can be used in your data backup system. Every approach comes with its own set of pros and cons, so the most suitable method will vary based on your company’s requirements.
Step 4: Put the data backup strategy to the test
Finally, it is important to review backups on a regular basis to ensure that they are ready for recovery. This will help to guarantee that the company is prepared in the event of a breakdown or disaster, lowering the risk of data loss and reducing the time it takes to restore systems and data. If any problems develop, you can change your data backup strategy to address them and improve reliability over time.
Disaster recovery for business continuity
While backups are an extremely important part of operating your system, let’s take a look at the bigger picture of disaster recovery planning. A backup is a key factor in this since data is the lifeline of your business, but the data is of no use if you don’t have a system to access it. Experiencing downtime in your systems will result in a decrease in revenue, therefore, it is crucial to quickly recover to minimise losses.
Disaster planning must consider more than just creating backups. Bigger companies, like financial institutions, typically have emergency plans in place called ‘hot recovery’ which consist of a backup site ready to take over operations immediately in case of any issues with the main system. However, smaller businesses may find this option impractical or too costly, yet it is important to have a contingency plan in case of a serious issue.
Conclusion
In conclusion, we’ve provided all the essential points you need to create an effective and reliable backup plan for your business. From understanding the differences between cloud storage and cloud backup to identifying what data needs to be backed up and planning for disaster recovery, you now have the tools to safeguard your business from data loss and downtime.
If you have any questions, need guidance, or want professional support to ensure your data is fully protected, don’t hesitate to get in touch with us. We’re here to help you create a backup plan that fits your business’s unique needs, so you can focus on growth and success with total peace of mind.
Download our free Disaster Recovery Plan Checklist
Ensure your disaster recovery plan checks all the boxes, to be well prepared.